The terms "data" and "statistics" are often used interchangeably. However, in practice, they mean two different things. Data is the raw information from which statistics are derived. Put in the reverse, statistics provide an interpretation and summary of data. Statistics are the numbers and percentages found in academic journal articles, magazines, and newspapers. Datasets must be collected or downloaded and independently analyzed.
If you’re looking for a quick number, you want a statistic. A statistic will answer “how much” or “how many”. A statistic repeats a pre-defined observation about reality.
Statistics are the results of data analysis. They usually come in the form of a table or chart. This is what a statistical table looks like:
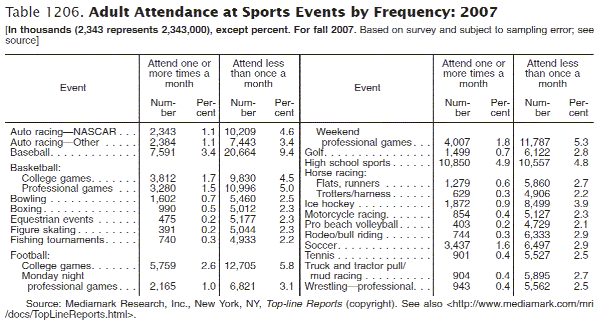
Source: Statistical Abstract of the United States
If you want to dig into a phenomenon, you want data. Data can be analyzed and interpreted using statistical procedures to answer “why” or “how.” Data is used to create new information and knowledge.
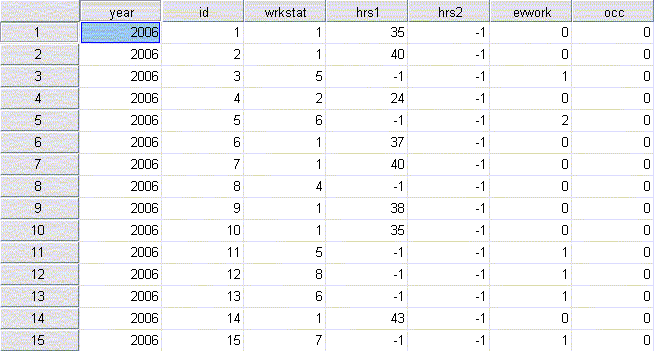
Raw data is the direct result of research that was conducted as part of a study or survey. It is a primary source. It usually comes in the form of a digital dataset that can be analyzed using software such as Excel, SPSS, SAS, and so on. This is what a dataset looks like: